Coal processing is a long series of processes to convert raw coal into stable electrical energy for society and industry. Starting from mining, transportation, burning, to electricity distribution, each stage requires technology and strict operational standards. In Indonesia, processed coal is still the foundation of energy security because of its large supply, stable prices, and ability to meet national electricity needs. This article discusses the coal processing process from upstream to downstream, complete with benefits, challenges and national energy context.
Why Still Coal?
Indonesia still relies on coal as the backbone of national energy for several strategic reasons:
- Abundant reserves: Indonesia has 41.5 billion tons of coal reserves (ESDM, 2024), making it one of the countries with the largest reserves in the world.
- Stable price and availability: Coal production costs and selling prices are relatively cheaper compared to other fossil energies.
- Generator dependency: More than 60% of national electricity generation still relies on processed coal as primary energy.
- Complete infrastructure: Supply chain and mine mouth power plant make operations more efficient.
This condition means that coal processing methods remain relevant in ensuring the national electricity supply, even when Indonesia begins to enter the energy transition era.
Also Read Coal Downstreaming Accelerated, PTBA and BRIN Develop Coal as Raw Material for Lithum Batteries.
Coal Processing Process to Produce Electricity
The following are the complete stages from upstream to downstream, starting from when coal comes out of the earth until it becomes electricity.
1. Coal Mining Process
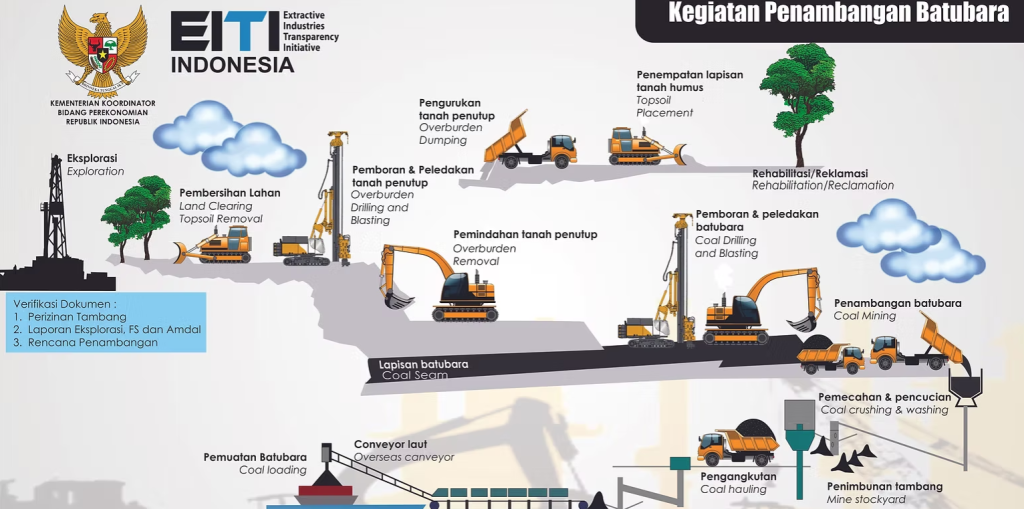
Indonesian coal mines generally use the open pit method because of cost efficiency. At this stage:
- Shovels, excavators and dozers work 24 hours digging coal from the mine pit.
- The material is transported by dump truck to the stockpile as the initial stage of coal processing.
- National production in 2024 will reach 836 million tons, equivalent to 7 times the weight of the entire human population on earth.
This stage is the foundation of the coal processing method because the quality of the coal is determined from the extraction process.
2. Transported to the Power Plant
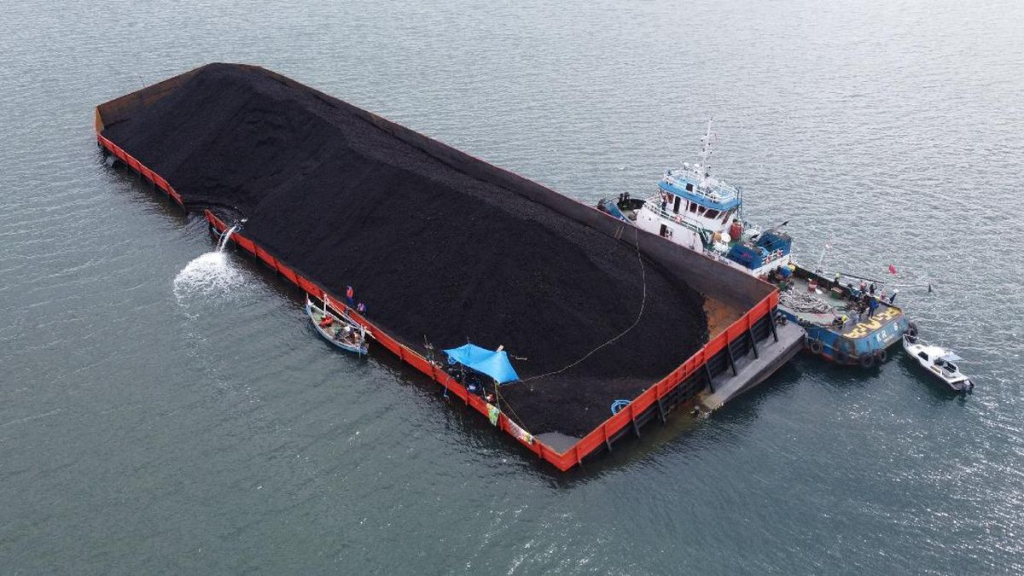

After production, the processed coal is transferred to the PLTU via:
- Special truck for short distances
- Coal train
- Barges travel by river and sea
Along the logistics route, coal:
- Collected in stockpile
- Through a crusher plant for size reduction
- Specifications can be adjusted according to the needs of the combustion system
This model keeps logistics costs low, especially at mine mouth PLTU.
3. Process of Burning Coal to Make Electricity
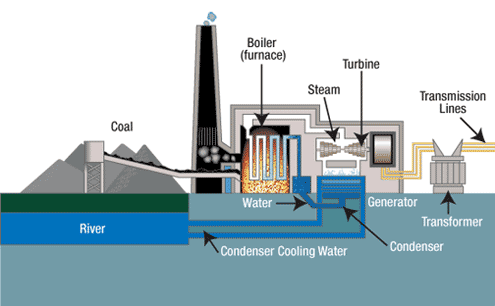
At the PLTU, coal undergoes the main energy processing processes:
- Coal is burned at temperatures over 1,000°C
- The heat turns the water into high pressure steam of 170 bar
- The steam turns a high-speed turbine
- The turbine drives the generator rotor to produce electricity
This stage is the core of processing coal into electricity which supplies national needs.
4. Electricity is distributed to your house
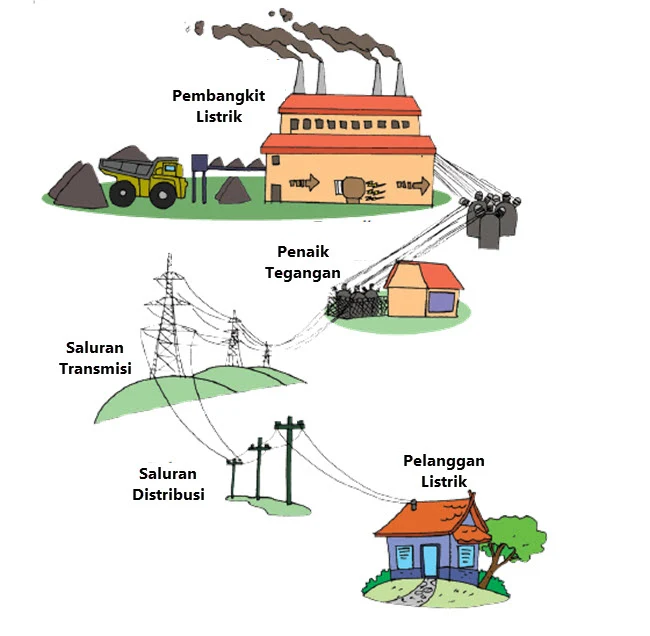
After electricity is generated at the PLTU:
- The voltage is increased via a step-up transformer
- Distributed via PLN’s high voltage transmission network
- Lowered the voltage at the substation
- Distributed through the distribution network until it arrives at people’s homes
With this series, the processed coal products can be used directly by end users.
Also Read: Get to know Metallurgical Coal: High Selling Price Coal
What are the products of processed coal?
Apart from being fuel for PLTUs, coal processing produces several important products:
1. Fly Ash & Bottom Ash (FABA)
Combustion residue products for construction materials such as concrete, cement and paving blocks.
2. Coal Briquettes
Processing low calorie coal into briquettes for small industries and households.
3. Liquid Coal (Coal Liquefaction)
Technology converts coal into synthetic liquid fuel.
4. Coal Gasification
Transformation of coal into syngas for the petrochemical and energy industries.
These products expand the benefits of coal and support the sustainability of national industry.
Conclusion
Coal is often considered dirty energy because of its high carbon emissions, but in reality coal is still a pillar of national energy security. Large availability, stable prices and mature infrastructure mean that coal is still an important pillar of electricity supply.
Indonesia still needs to encourage the use of clean burning technology, increase the efficiency of PLTUs, and expand EBT. With these steps, coal processing can still be used responsibly while supporting the transition process towards clean energy in the future.
Source: www.minercomedia.com