After discussing the exploration stage, let’s get to know the next stage. This is the process of utilizing and producing resources that have been discovered. This stage is divided into 2 parts, namely the Development Stage (POD) for 3-6 years and the Production Stage for 14-17 years.
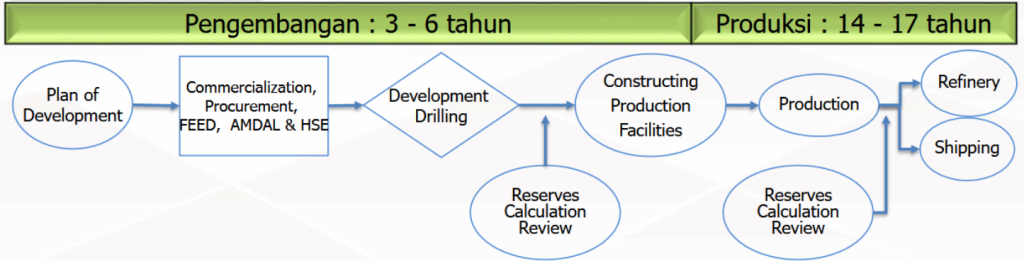
Development Phase (3 – 6 years)
This phase consists of several parts as follows:
- Plan of Development (POD)
POD (Field Development Plan) is an official document that explains the overall plan for the development of an oil and gas field from start to finish. This document covers all technical, economic, regulatory aspects, as well as environmental and social impacts. Submission of POD documents by Cooperation Contract Contractors (KKKS) must obtain approval from the government or oil and gas authority, namely SKK Migas in Indonesia before entering the development stage.
- Commercialization, Procurement, FEED, AMDAL & HSE
Commercialization is the determination of sales strategies for hydrocarbons to be produced, including sales contracts and potential markets. This aspect generally occurs in gas field development
Procurement (Procurement) is the provision of tools, materials and services required for development drilling and construction of production facilities.
FEED (Front-End Engineering Design) mis the process of designing technical concepts and designing production facilities to be built, including platforms, pipeline networks and oil/gas processing systems.
AMDAL (Environmental Impact Analysis) is mandatory study of the environmental impact of the entire project based on environmental regulations in accordance with KLHK standards
HSE (Health, Safety and Environment) are safety and health standards that are applied to all crew to ensure safe operations and ability to face uncertain work risks.
The development well drilling stage is carried out as an initial production well to extract large quantities of hydrocarbons and ensure production sustainability. This stage is very important because the success of field development depends on the design and location of the production well. It is important to remember that drilling exploration wells and development wells are two different things. The development well will be drilled if the exploration well drilling assessment results show adequate hydrocarbon production
- Evaluation of Reserve Calculations
Previously calculated hydrocarbon reserves will be reviewed based on new and more extensive data from development well drilling. The calculation results can show results that are smaller or larger than the initial calculation, but calculations at this stage have smaller uncertainties.
- Construction of Production Facilities
The final stage in the development phase is the construction of field-scale production facilities such as offshore platforms (for offshore fields), oil and gas processing systems, pipeline systems, storage tanks, etc. Please note that this stage requires a large investment so it will take quite a long time. Constructed surface facilities must comply with technical standards, safety and government regulations.
Production Phase (14 – 17 years)
This phase consists of several parts as follows:
At this stage, hydrocarbon production has been carried out through drilling of previous development wells. The production system includes separation of oil, gas and water, as well as initial processing before sending to the refinery for refining.
At the production stage, reservoir pressure will tend to decrease as time goes by. Therefore, production optimization is carried out at this stage such as pressure maintenance (waterflood), artificial lift method, stimulation, tertiary recovery (EOR)
- Evaluation of Reserve Calculations
The ongoing production phase provides more data with a lower level of uncertainty. Periodic reserve reviews of remaining oil and gas reserves need to be carried out to determine whether the field is still economical to continue producing or whether optimization needs to be carried out. If production decreases drastically, strategies to extend the life of the field can be implemented, such as drilling additional wells or injecting water/gas as a pressure buffer.
The crude oil produced will be sent to refineries for the refining process into petroleum products such as gasoline, diesel and other fuels. The refining process includes the separation of crude oil fractions based on boiling point, as well as the conversion of heavy hydrocarbons into lighter fuels. The gas produced can also be purified to remove impurities such as CO₂ and H₂S before use so that it is suitable for sales products.
- Distribution and Shipping
After refining, oil and gas products are distributed to various destinations, both for domestic and export markets. Oil and gas transportation can be done via pipeline, tanker, or truck depending on location and market needs. Generally, Indonesia has excess production of LNG type natural gas so that it can be compressed for export and sent to other countries.
Source: www.minercomedia.com